What Is Diagnostic Imaging?
Diagnostic health imaging technology has transformed healthcare and now allows for earlier diagnosis of medical conditions, reduces the need for needless invasive exploratory processes and creates better patient outcomes. Health Images offers comprehensive diagnostic imaging services.
Let’s explore diagnostic imaging in more detail and learn about the different types of imaging.
Jump to Sections:
- What Is Diagnostic Imaging?
- What Is Diagnostic Imaging Used For?
- Types of Diagnostic Imaging
- MRI Scans
- MRA Scans
- CT Scans
- Ultrasounds
- X-rays
- Mammography
- Bone Density Scans
- Arthrogram
- Myelogram
What Is Diagnostic Imaging?
Diagnostic imaging describes various techniques of viewing the inside of the body to help figure out the causes of an illness or injury and confirm a diagnosis. Doctors also use it to see how well a patient’s body responds to treatment for a fracture or illness.
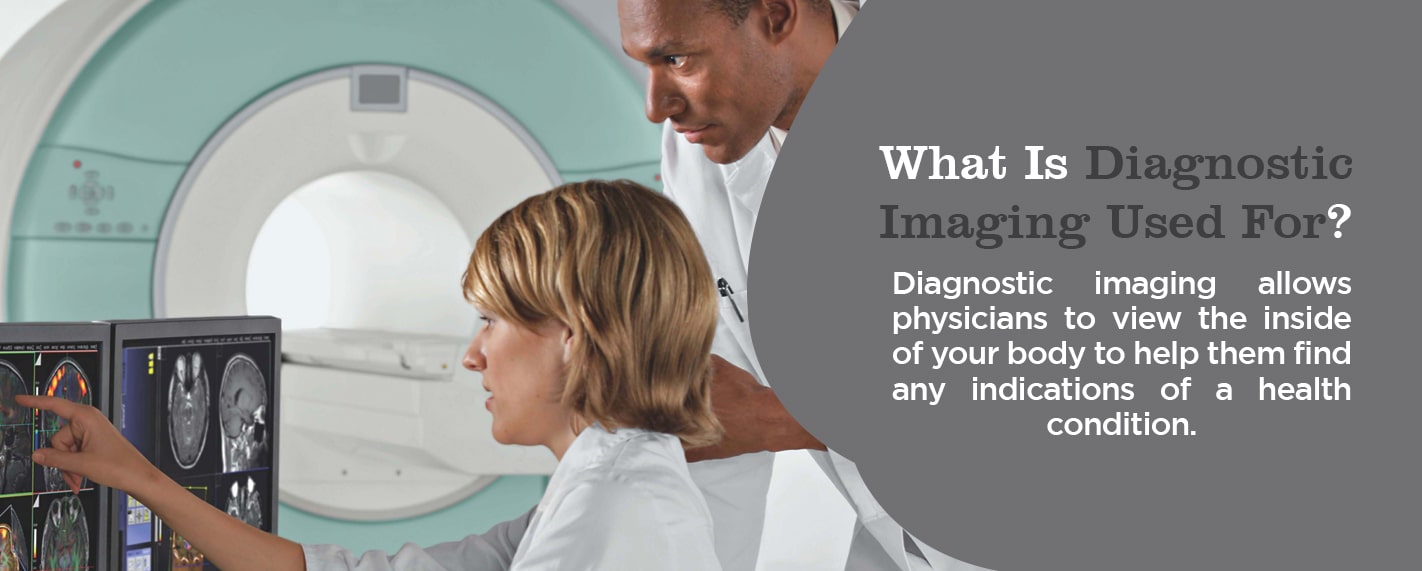
What Is Diagnostic Imaging Used For?
Diagnostic imaging allows physicians to view the inside of your body to help them find any indications of a health condition. Some machines and methods can produce pictures of the activities and structures inside your body. Your doctor will decide which medical imaging tests they’ll need to use based on the body part they’re evaluating and your symptoms.
Many imaging tests are noninvasive, easy and painless. Some will require you to remain still inside the machine for a long time, however, which can get a little uncomfortable. Some tests involve a small amount of radiation exposure.
For other imaging tests, the doctor will insert a small camera attached to a thin, long tube into your body. This device is referred to as a “scope.” They’ll then move the scope through a bodily opening or passageway to view the inside of a particular organ, like your lungs, heart or colon. You may need anesthesia for these procedures.
Types of Diagnostic Imaging
Health Images offers a full array of diagnostic imaging services, including the following.
1. MRI Scans
MRIs don’t use radiation, but rather a powerful magnet to obtain an image of the body of the patient. There are four types of MRI machines:
- True open: The true open mri design is open on all sides. It removes a lot of the discomfort for individuals who get claustrophobic in a regular MRI machine.
- Closed: This closed machine — or traditional tube machine — is one in which you lie down and go inside for the images.
- 3T: The “T” means Tesla and is a unit of measurement the technologist uses to quantify the magnetic field strength. The 3T MRI is the most innovative and advanced test of all the MRIs used today. It’s a closed design, like the traditional MRI. It takes less time to perform the test using the 3T MRI, and the images are detailed and high-resolution, enabling the radiologist to determine whether you have a benign or more severe medical condition.
- Wide bore: Sometimes called an “open MRI,” this machine resembles a closed MRI, but with a wider opening.
Your doctor might recommend an MRI scan for numerous reasons. It provides them with an incredibly detailed look inside your body, and they can use it to examine things like:
- Spinal cord and brain anomalies
- Cysts, tumors and other bodily irregularities
- Joint abnormalities and injuries
- Breast tissue to screen for cancer
- A woman’s pelvic area to identify issues like fibroids and endometriosis
- Suspected uterine anomalies
- Abdominal or liver diseases
- And a lot more — MRI technology use is continually expanding
An MRI exam generally takes about 30 to 60 minutes from beginning to end. The doctor might include contrast, or fluid injected into your vein to make specific details clearer in the generated images. This step can make the exam last longer.
2. MRA Scans
MRA stands for magnetic resonance angiogram, a test that provides very detailed images of the blood vessels in the body. MRA scans are a form of MRIs.
Using radio wave energy pulses and a magnetic field, the MRA provides information that CT scans, ultrasounds or x-rays can’t always obtain. MRA tests are typically used on the legs, neck, brain and kidneys to collect information about the condition of blood flow and blood vessel walls. Doctors also use MRAs to look for calcium deposits, aneurysms and clots within the blood vessels. In some cases, they may order a contrast dye to get a better definition in the scan’s images of your blood vessels.
MRA scans offer definite benefits to both patients and doctors, who use the images for diagnosing health problems. These benefits include the following:
- They don’t use radiation, unlike CT scans and x-rays.
- They’re non-invasive.
- In many cases, an MRA scan can detect information that x-rays, ultrasounds and CT scans miss.
- MRA scans can detect issues with blood vessels that lead to reduced blood flow.
An MRA scan is a helpful diagnostic tool with the main purpose of finding issues that might exist within the blood vessels. These scans are commonly used for:
- Detecting calcium deposits, aneurysms or clots in blood vessels
- Finding existing blood vessel narrowing
- Identifying abnormalities in the blood vessels of the brain, like congenital disabilities and inflammation
- Defining blood supply to the brain’s vascular tumors
- Evaluating stroke patients
- And much more
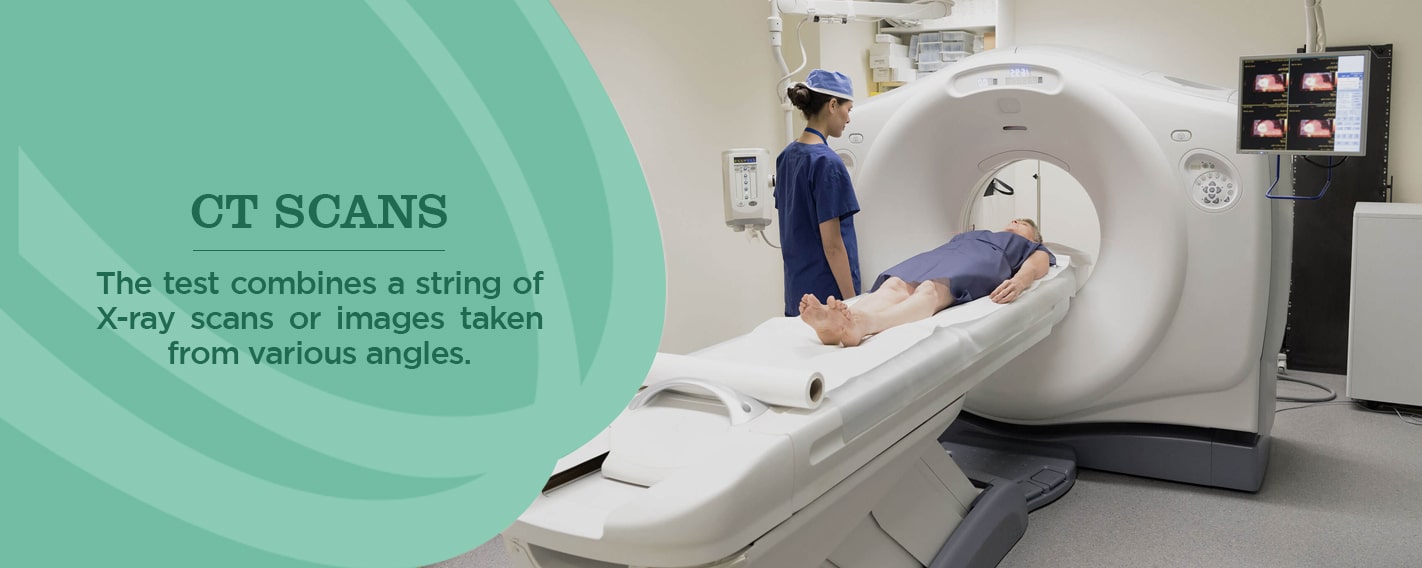
3. CT Scans
Physicians also refer to a CT scan as a “cat scan.” The test combines a string of X-ray scans or images taken from various angles. Computer software then generates cross-sectional images (slices) of blood vessels and soft tissues inside the body. CT scans can offer a more thorough picture than standard X-rays. They’re frequently used to quickly examine individuals who have internal injuries from a trauma.
Doctors can use CT scans to evaluate the spine, brain, abdomen, neck and chest. They provide clear images of both hard and soft tissues. The pictures the CT scans produce allow doctors to quickly make medical decisions if required. Because of this quality, CT scans are commonly performed in both imaging centers and hospitals. They help physicians find injuries and diseases that could previously only be found in a surgery or autopsy. While CT scans use low doses of radiation, they’re still relatively non-invasive and safe.
These scans are useful in a variety of medical situations where diagnostic imagery is required. They can assess slight abnormalities in soft tissue like the brain as well as other organs. Doctors also use the images when patients have certain symptoms like dizziness or pain. They’re even useful in examining the spread of certain conditions, such as cancer. Depending on where the technologist directs the CT scan in your body, there are various uses for it, including:
- Brain or head CT scans: Check for stroke, bleeds, masses and other abnormalities and examine the skull
- Chest CT scans: Provide further insight into abnormalities after a standard chest x-ray
- Neck CT scans: Look for enlarged glands or lymph nodes and study lumps.
- Spine CT scans: Detect spine problems like spinal canal narrowing, a herniated disc or fractures
- Sinus CT scans: Detect and diagnose obstructions or sinus disease
- Pelvic or abnormal CT scans: Check organs in this area and diagnose unexplained pain in the abdomen
4. Ultrasound
Also referred to as “sonography,” ultrasound imaging is a safe imaging method that creates images of the inside of the body. It doesn’t use radiation, but rather high-frequency waves. As a result, it’s a safe procedure during pregnancy. The ultrasound images are in real-time and show the structure and movement of internal organs and the blood flow through vessels.
During an ultrasound, a sonographer will hold a transducer — a handheld device — over your skin. Sometimes it’s placed internally. It uses sound waves traveling through soft tissue and fluids, and as it hits denser surfaces, it echoes or bounces back, which is how the images are created. More ultrasound echoes back when the object is denser.
Doctors can diagnose a large variety of health conditions with an ultrasound. The images it creates also help physicians come up with treatment plans. If you have symptoms such as swelling, infection or pain, your doctor might suggest an ultrasound to determine the cause. Ultrasounds are also used to assist anesthesiologist during surgical procedures when they’re guiding needles near nerves.
In a lot of cases, ultrasounds are tools that allow doctors to examine problems related to abdominal issues, circulation, urology, obstetrics, newborn care and even musculoskeletal conditions. Some common body parts physicians use ultrasounds for include:
- Heart
- Joints
- Uterus
- Blood vessels
- Muscles
- Bladder
- Kidneys
- And more
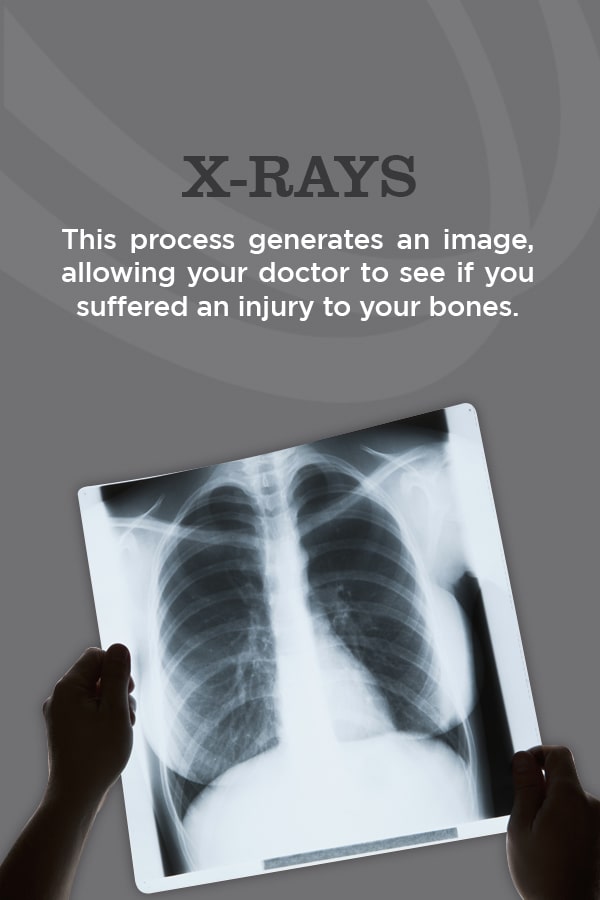
5. X-rays
X-rays are among the most commonly used and well-known diagnostic imaging tests. Doctors use them to view the inside of the body. X-ray equipment generates a high-energy beam that dense tissue and bones can’t absorb, but that passes through other areas of the body. This process generates an image, allowing your doctor to see if you suffered an injury to your bones.
6. Mammography
Mammograms are a type of x-ray image of the breasts. They check for early breast cancer signs like small lumps you or your doctor can’t feel through the use of a low-dose x-ray. Mammograms also show breast tissue changes that could be a sign of early-stage breast cancer.
A radiologist uses digital mammography to identify and diagnose cancer nodules that older systems can’t detect. Mammograms are the best way to detect early breast cancer because — in some cases as much as a few years before you can feel it. Having mammograms regularly comes with various benefits, including the following:
- They detect breast cancer early on, which saves lives.
- They reduce your risk of dying because of breast cancer by 30 percent.
- Getting treatment early means you can keep your breasts and don’t have to resort to mastectomy.
Mammograms, to some women, can be uncomfortable and sometimes even painful. A lot of this feeling depends on how big your breasts are and the amount of pressure needed to be applied. The discomfort will last only a few minutes, and the fact that this procedure can save your life makes it worth it.
7. Bone Density Scans
A bone density scan is an indirect test that physicians use to determine whether or not you have osteoporosis. The procedure is also referred to as “bone mineral density testing,” and it measures the amount of bone material you have per square centimeter in your bones.
Osteoporosis is a condition that makes the bones fragile and susceptible to fractures. A bone density scan uses x-ray equipment to measure the bone minerals and calcium packed into a small bone segment. Typically, you’ll have this scan conducted on your hip, spine or forearm. Your bones are denser if you have higher bone mineral content, meaning they’re less likely to break. The bones are at risk of being fractured if they have a low bone mineral content, which can indicate osteoporosis.
Prior to using a bone density scan, the only way doctors could diagnose a patient with osteoporosis was if they broke a bone. At this point, the bones would already be weakened by the condition and in a poor state. Older women are more at risk for this disease, but anyone can develop the condition, no matter their sex or age.
Your physician might suggest a bone density scan if you have the following risk factors:
- Fragile bones that are more susceptible to fractures
- Reduced height of a minimum of an inch and a half
- Lowered sex hormone levels
- The need for certain medicines that interfere with the rebuilding process of your bones, like steroids
- The need for anti-rejection medication after a transplant
8. Arthrogram
When your joints are not functioning as they should be, it stops your movement ability and makes daily tasks harder. An arthrogram is one of the various types of medical imaging used for diagnosing joint problems that other types of imaging might not be able to detect. Also referred to as “arthrography,” arthrograms consist of various images taken using x-ray, fluoroscopy, CT scans or an MRI specifically of the joints.
The radiologist will inject your joint with a contrast dye such as iodine before your arthrogram. They’ll use a fluoroscope to guide the injection placement into your joint. This dye will coat your joint structure linings, making them look white on the images and highlighting any problems so that the doctor can evaluate the function of the joint and come up with a diagnosis.
9. Myelogram
When the doctor needs specific imaging of the spinal canal, like the spinal tissue, spinal cord and surrounding nerves, they’ll order a myelogram. A myelogram is an exam during which the technologist injects contrast dye into the spinal cord space while using fluoroscopy to take moving x-ray images. As this dye flows through the spaces, the doctor will examine the area for any abnormalities, including tumors, infection and inflammation.
A CT scan typically follows a myelogram procedure to help better define any possible issues. Combined with CT technology, myelograms can give your doctor more detailed information than they would get with x-rays alone.
Schedule Your Diagnostic Imaging Appointment Today
Now that you have your “What is diagnostic medical imaging” question answered, it’s time to schedule your appointment. Contact Health Images for your diagnostic imaging needs. We have various convenient locations in Colorado, including Boulder, Denver, Longmont and Castle Rock. Our specialized staff members are ready to help you with all your diagnostic imaging needs.
Sources:
- https://mifimaging.com/2017/04/17/what-is-diagnostic-imaging/
- https://www.rasmussen.edu/degrees/health-sciences/blog/types-of-diagnostic-imaging/
- https://www.floridamedicalclinic.com/blog/what-is-diagnostic-radiology/
- https://www.envrad.com/services/x-ray/
- https://www.envrad.com/services/mammography/
- https://www.envrad.com/services/mra-scans/
- https://www.envrad.com/services/mri-scans/
- https://www.envrad.com/services/ultrasound-sonogram/
- https://www.healthimages.com/services/ct-scans/
- https://www.healthimages.com/services/bone-density/
- https://www.healthimages.com/services/arthrograms/
- https://www.healthimages.com/services/myelogram/
- https://www.healthimages.com/locations/
- https://www.healthimages.com/about-us/why-choose-us/