Types of Preventative Imaging
It is well known that medical imaging is a strong tool for helping patients understand their health by providing a detailed look inside the body. But how can this technology be used to prevent health issues before they develop? To answer this question, we’ll dive into what preventative imaging is, why it is important, the contrast of preventative vs. diagnostic imaging and a few of the most common types of preventative imaging.
What Is Preventative Screening?
Preventative imaging focuses on testing for a specific disease in hopes of detecting it early for more effective treatment. When a disease is discovered in its earliest phase, it can be treated before it is fully developed and kept from growing into a worse issue. Even if the condition cannot be completely cured, treating a chronic disease early can keep symptoms to a minimum.
Diseases typically become more and more deadly as they progress, but preventative imaging can help patients get on the right treatment plan as soon as possible. In addition, preventative imaging can provide valuable information to doctors, researchers and other medical professionals. The data produced by preventative imaging can help lead to the development of improved medical treatment and tools.
Preventative care procedures can include screenings, lab tests and immunizations, each of which can detect health problems before the patient has begun experiencing any symptoms. By working to prevent an illness, this type of imaging can help save patients’ lives and keep them healthy when conducted at the right time.
Regular preventative screening tests may be recommended for a patient if they have a family history of a certain condition or check off other risk factors for a condition, such as age, gender or preexisting related diseases. By scheduling an annual screening for diseases they may be prone to, patients can help ensure they stay well and catch any serious illnesses early enough to begin an effective treatment plan.
How Does Preventative Imaging Differ From Diagnostic Medical Imaging?
Although it can be difficult to discern the difference between preventative imaging and diagnostic imaging considering their many similarities, there are plenty of differentiating qualities between them. Whereas preventative imaging is intended to detect health problems before the disease’s symptoms develop into more serious health issues, diagnostic imaging is designed to diagnose or treat symptoms that already exist in the patient.
Usually, patients receive preventative care during a regular checkup. If an abnormality arises during the preventative screening, further diagnostic imaging may be needed to reach more conclusive results. Preventative imaging is typically a routine screening of some sort, such as a mammogram, whereas diagnostic imaging is scheduled to investigate a problem further, such as a mammogram to follow up on an abnormal breast lump.
In this way, preventative care and diagnostic medical imaging can work in tandem. Preventative screening tests can alert patients and their doctors of any medical red flags, while diagnostic imaging can act as a follow-up to any preventative procedure results that may be cause for concern. A more detailed diagnostic imaging test can provide more insight into the reason behind an abnormality.
Additionally, a diagnostic imaging test may be recommended to a patient if they are experiencing symptoms but are uncertain of the cause. The right imaging test can help determine the root cause of unfamiliar symptoms. For instance, a patient might receive a colonoscopy to evaluate unexplained rectal bleeding. Diagnostic imaging may also be used to monitor existing health issues to ensure they do not worsen.
Types of Preventative Imaging
There are numerous types of preventative imaging tests a patient may undergo. Each patient’s unique medical history and past health conditions will determine which routine preventative imaging screenings they should schedule for themselves. Below are three of the most common types of preventative imaging procedures and their purposes:
1. Full-Body MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) test is a noninvasive scan involving strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the inside of the body, which can be used to evaluate the body’s soft tissues. Because inflammation and tumors produce a higher amount of water and swelling, an MRI can indicate abnormal areas of water accumulation and swelling, leading to a preemptive detection of a disease.
In addition to detecting tumors, a full-body MRI delivers a comprehensive look at the soft tissues throughout the body for other abnormalities including:
- Cysts and other irregularities
- Joint injuries or abnormalities
- Liver issues and other abdominal diseases
- Brain or spinal cord abnormalities
- Uterine abnormalities
- Causes of pelvic pain in women, such as fibroids or endometriosis
- Other health issues
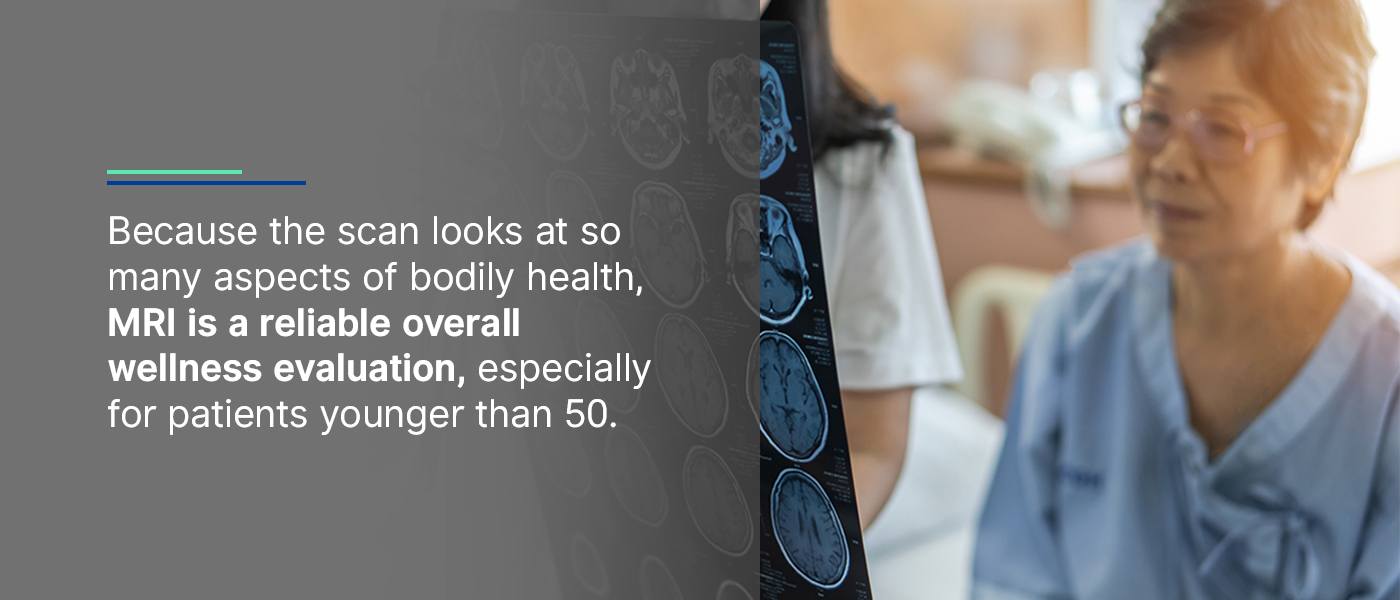
Because the scan looks at so many aspects of bodily health, it is a reliable overall wellness evaluation, especially for patients younger than 50. Those with a family history of stroke, neurological problems or cancer should also consider a full-body MRI. This test is also an effective diagnostic imaging method for examining symptoms like unexplained pain, weight loss, fatigue or joint problems.
2. Cardiac Score
Because an excess of plaque or calcium in the arteries can result in serious health issues like heart disease or a heart attack, it is important to be aware of how much buildup is present. Although a buildup of plaque or calcium in the arteries can be difficult to detect, a cardiac score uses computed tomography (CT) scan technology to enable a doctor to determine how much artery buildup is present. This can affect what steps a doctor recommends taking next in a patient’s health care journey.
Essentially, cardiac scoring is a CT scan of the chest that looks for any narrowing of the heart’s arteries. By taking multiple images of the coronary arteries, the test can come up with a specific cardiac score that indicates the level of buildup in the arteries and where it is located.
Cardiac scoring is an important component of preventative care because coronary calcium scoring can be greatly predictive of obstructive coronary artery disease. Plaque buildup is dangerous because it can narrow the arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart, which may cause a heart attack.
The result from cardiac scoring paired with more traditional cardiac risk factors, such as diet and family medical history, help determine a patient’s cardiovascular risk. Older patients with an increased risk of heart issues due to diabetes, smoking, high blood pressure or another factor would benefit highly from cardiac scoring.
3. Routine Mammograms
A mammogram is a type of breast imaging that produces an x-ray image of the breast. By using a low dose x-ray, a mammogram can detect the earliest signs of breast cancer, such as breast lumps that are not yet big enough for patients or a medical professional to feel. Additionally, a mammogram can show doctors whether there are any changes in the breast tissue, which is another warning of developing breast cancer.
Because a mammogram can catch breast cancer early before it becomes a more life-threatening issue, scheduling a routine mammogram is a great habit for older women. In fact, regular mammograms reduce the risk of dying from breast cancer by up to 30%. Also, treating breast cancer early can decrease the need for a mastectomy, allowing women to maintain their breasts.
Schedule Your Preventative Imaging Appointment at Health Images
If you’re looking for a reliable radiology center where you can receive preventative imaging quickly and efficiently, schedule an appointment with Health Images. At Health Images, we offer spectacular services and compassionate care to ensure each patient has a pleasant and accurate experience. Because we accept a wide variety of insurance plans, our high-quality imaging services are affordable and accessible.
To book your preventative imaging, find the Health Images location nearest you today.